Funded Research Projects
|
No. |
Project Title |
Role |
Start Year |
Source of Funding |
Total Budget (€) |
Budget for Host (€) |
|
1 |
Retrofitting of RC Buildings with RC infills |
Coordinator |
2013 |
Research Promotion Foundation |
30,000 |
30,000 |
|
2 |
Seismic Safety and Vulnerability Mitigation of School Buildings |
Coordinator |
2010 |
Research Promotion Foundation |
160,000 |
80,000 |
|
3 |
Seismic Strengthening of Deficient RC Buildings Using Ductile
Post-Tensioned Metal Strips |
Partner |
2010 |
7th Framework Program |
500,000 |
30,000 |
|
4 |
Seismic Retrofitting of RC frames with RC infilling (SERFIN) |
Coordinator |
2009 |
7th Framework Program |
600,000 |
600,000 |
|
5 |
Smart Management for sustainable Human Environment (SmartEN) ITN |
Member of CUT team |
2009 |
7th Framework Program |
3,700,000 |
640,000 |
|
6 |
Earthquake Model of the Middle East Region (EMME) |
Partner |
2009 |
Japanese Tobacco Industries |
2,000,000 |
17,000 |
|
7 |
Seismic Vulnerability and Strengthening
of Existing Privately Owned Buildings |
Coordinator |
2008 |
Research Promotion Foundation |
140,000 |
48,000 |
|
8 |
Earthquake Vulnerability Assessment of Historical Monuments |
Partner |
2008 |
European Commission |
215,000 |
80,000 |
|
9 |
Training of Civil Engineers on Post-Earthquake Safety Assessment
of Damaged Buildings (TRIPOD) |
Partner |
2006 |
Leonardo Da Vinci |
500,000 |
75,000 |
|
10 |
Wide-Range Non-Intrusive devices toward Conservation of
Historical Monuments in the Mediterranean Area (WIND-CHIME) |
Partner |
2004 |
6th Framework Program |
1,000,000 |
160,000 |
|
11 |
Seismic performance assessment and rehabilitation (SPEAR) |
Partner |
2002 |
5th Framework Program |
900,000 |
78,000 |
|
12 |
Hazard analysis of the City of Nicosia |
Associate Partner |
2002 |
UNOPS |
- |
55,000 |
|
13 |
Conservation of Historical Mediterranean
Sites by Innovative Seismic-Protection Techniques (CHIME) |
Partner |
2000 |
5th Framework Program |
800,000 |
160,000 |
|
14 |
Restoration and Maintenance of Traditional Settlements |
Associate Partner |
2000 |
UNOPS |
76,000 |
76,000 |
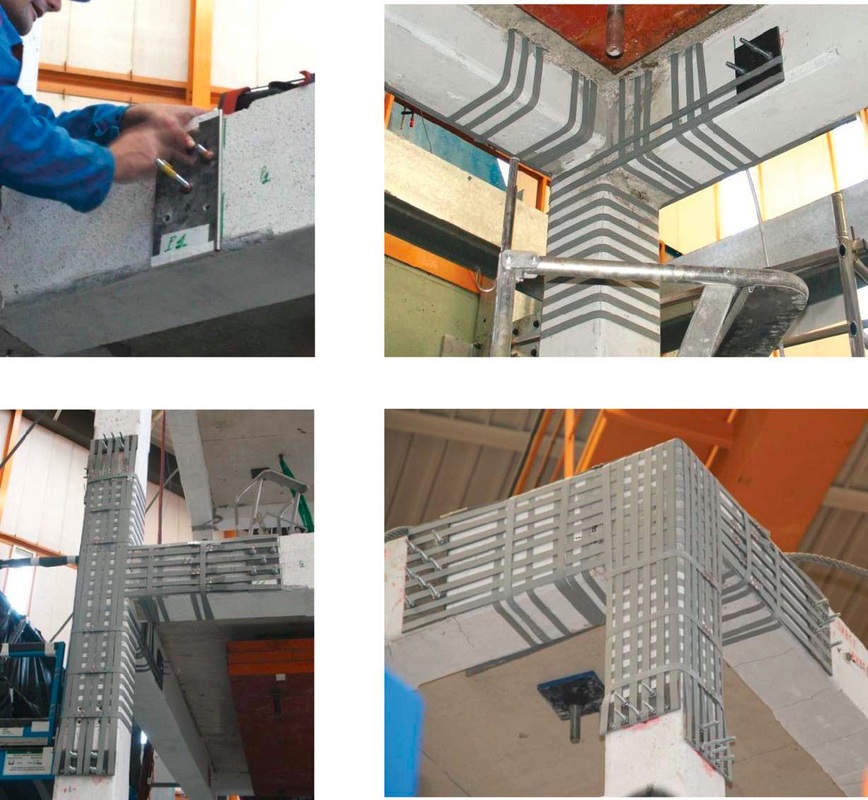
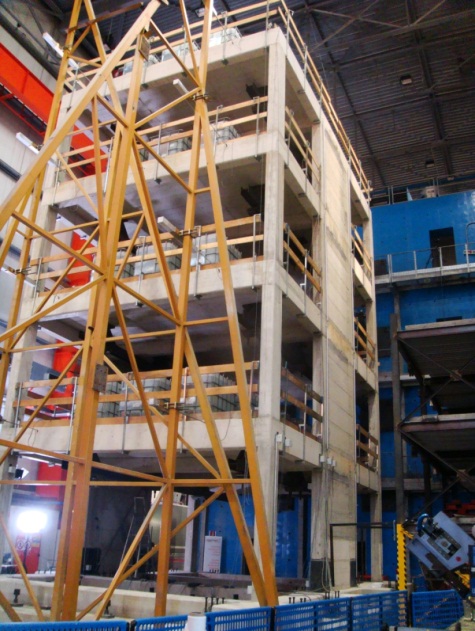
Retrofitting of RC Buildings with RC infills
Cyprus University of Technology (CY, coordinator)
Ecole Centrale de Nantes (FR)
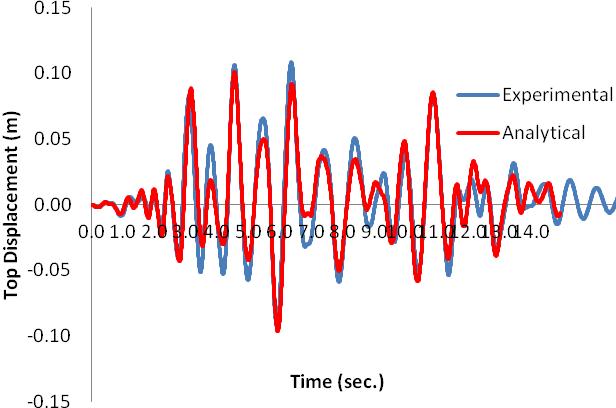
Comparison of experimental vs analytical response of the tested specimen
Seismic Safety and Vulnerability Mitigation of School Buildings
Cyprus University of Technology (CY, coordinator)
Aristotle University of Thessaloniki (GR)
SignalGeneriX ltd (CY)
Technical Services of the Ministry of Education of Cyprus (CY)
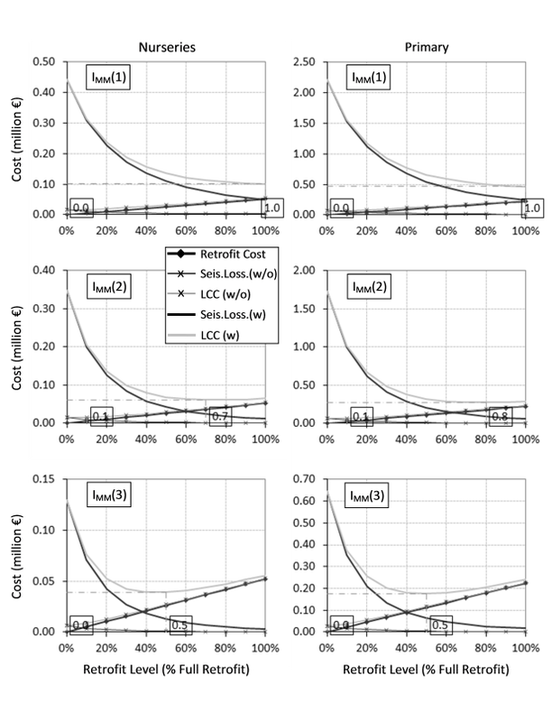
To answer the above questions the following objectives were specified: a) propose a methodology for examining the effectiveness of retrofitting in increasing the seismic safety and reducing the vulnerability of schools, b) use of in-situ measurements for the updating of mathematical models of structures and c) propose a methodology for rational decision making for future strengthening, taking into account economic and technical factors.
Seismic Strengthening of Deficient RC Buildings Using Ductile Post-Tensioned Metal Strips
University of Sheffield (UK, coordinator)
Cyprus University of Technology (CY)
The University of East London (UK)
Istanbul Technical University (TR)
Technical University of Iasi (RO)
University of Girona (ESP)
University of Nevada – Reno (US)
Seismic Retrofitting of RC frames with RC infilling (SERFIN)
Cyprus University of Technology (CY, coordinator)
University of Cyprus (CY)
University of Nantes (FR)
Denco (GR)
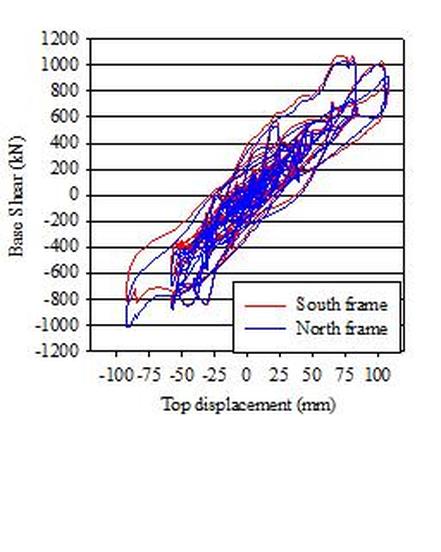
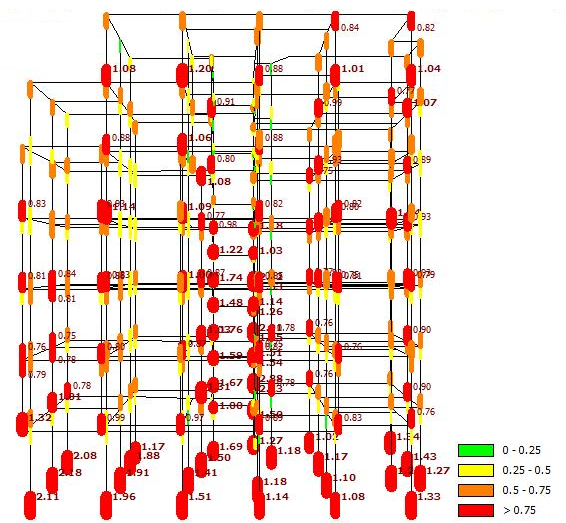
In order to start filling this gap of knowledge, it is proposed to study experimentally the effectiveness of seismic retrofitting of multi-storey multi-bay RC frame buildings by converting selected bays into new walls through infilling with RC. The full-scale test specimens will have the central bay infilled with RC wall. The specimens will be subjected to ground motions compatible with a target spectrum at different levels of peak ground acceleration. A test structure is proposed consisting of two parallel retrofitted frames, to be tested with the pseudo-dynamic method. The main parameters of the test structure will be the connection between the RC infill and the surrounding RC frame and the percentage of the reinforcement in the RC infill. The effect of these parameters will be studied during the experiment, by using different connection details and reinforcement percentages for the two infilled frames and/or at their different storeys.
Smart Management for sustainable Human Environment (SmartEN) ITN
Cyprus University of Technology (CY, coordinator Prof. Toula Onoufriou)
Research Academic Computer Technology Institute (GR)
Imperial College London (UK)
Research and Education Laboratory in Information Technologies (GR)
University of Surrey (UK)
University of Pavia (IT)
Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing (GER)
Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Testing and Research for Industry (SUI)
Ecole Nationale Supérieure des Télécommunications (FR)
Recently, a new generation of miniature wireless sensor platforms which utilize novel digital signal processing has emerged. These can be adopted to obtain large quantities of highly diverse sensor data that are continuously collected over a long period of time from multiple locations providing significant insight on the condition, demands and performance of the system. These developments open up a completely novel area of multidisciplinary research towards the ‘smart’ management of sustainable environment. Even though there are top research institutions working in the field of wireless sensors and others in the civil infrastructure reliability and management, most of the activity is fragmented and there is no significant activity in performing multidisciplinary structured research for developing integrated smart and dynamic systems for effective management of the built and natural environment. The aim of SmartEN is to fill this gap and push innovation through the development of an ITN network that will focus on the development and effective integration of emerging technologies targeting key application areas of current interest to the European Commission and internationally.
Earthquake Model of the Middle East Region (EMME)
ETH Zurich (coordinator)
Bogazici University (TR)
International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology (IRN)
Sakarya University (TR)
Middle East Technical University (TR)
Cyprus University of Technology (CY)
Yamouk University (JOR)
National Disaster Management Authority (PAK)
Atomic Energy Commission of Syria (SYR)
Georgian Academy of Sciences (GEO)
Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences (AZE)
Institute of Geological Sciences (ARM)
http://www.emme-gem.org/
Seismic Vulnerability and Strengthening of Existing Privately Owned Buildings
Cyprus University of Technology (CY, coordinator)
University of Cyprus (CY)
University of Patras (GR)
Cyprus Civil Defence (CY)
To meet the above requirements, the following objectives were set: a) determine the size of the problem presented to private buildings of Cyprus and particularly in Limassol, b) propose a methodology for rational decision-making for the upgrade of building-groups, taking into account economic, technical and local factors, and c) propose a financial-aid program for the upgrading of privately-owned buildings.
Earthquake Vulnerability Assessment of Historical Monuments
Union of Chambers of Cyprus Turkish Engineers and Architects (coordinator)
The Scientific and Technical Chamber of Cyprus
Training of Civil Engineers on Post-Earthquake Safety Assessment of Damaged Buildings (TRIPOD)
Computer Technology Institute and Press (GR, coordinator)
Technical Chamber of Greece/Department of Western Greece (GR)
Higher Technical Institute of Cyprus (CY)
Department of Civil Protection of Italy (IT)
Kandilli Observatory and Earthquake Research Institute of Bogazici University, Department of Earthquake Engineering (TR)
Some of the project objectives were:
- To combine existing methodologies and practices based on the roles of partners and their previous involvement in similar activities in order to create a common, unified core of knowledge about current practices for monitoring aftershocks buildings.
- To develop a comprehensive training methodology for engineering inspections, consisting of a model course, e-learning tool, and learning content.
- To develop an electronic learning environment this implements the above.
- To develop, with the help of e-learning platform 4 pilot courses, in 4 languages and organize on-line pilot training in participating countries based on these subjects.
- To produce and distribute content in traditional media (independent course in CD-ROM, manual pocket for civil engineers) in 4 languages (English, Greek, Italian, Turkish).
Wide-Range Non-Intrusive devices toward Conservation of Historical Monuments in the Mediterranean Area (WIND-CHIME)
Università Degli Studi di Pavia (IT, coordinator)
National Technical University of Greece (GR)
Institut National de la Météorologie (TUN)
Institut National du Patrimoine (TUN)
Jordan University of Science and Technology (JOR)
SIART – Sistemi Informativi per l’ Analyst del Rischio Territoriale ed Ambientale S.R.L. (IT)
SINTEF - Stiftelsen for Industriell og Teknisk Forsking ved Norges Tekniske Høgskole AS (NO)
Tallinna Tehnikauelikooli Kueberneetika Instituut (EST)
Themos Demetriou – Civil Engineer (CY)
Université de Tlemcen (DZA)
University of Cairo (EGY)
http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/74206_en.html
Seismic performance assessment and rehabilitation (SPEAR)
University of Patras (GR, Coordinator)
Università di Roma “La Sapienza” (IT)
Università Degli Studi di Pavia (IT)
University of Ljubljana (SVN)
Commission of the European Communities, JRC Ispra (IT)
Laboratório Nacional De Engenharia Civil (PT)
Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine (UK)
Higher Technical Institute (CY)
ABS Consulting ltd (UK)
It included 6 workpackages:
1) Conceptual framework and background of seismic assessment and rehabilitation;
2) Practical seismic assessment and rehabilitation;
3) Tests of RC members and small structures;
4) Pseudodynamic testing of large RC structure;
5) Proposals for seismic assessment and rehabilitation (for Eurocode 8); and
6) International cooperation (with USA, Japan and Turkey).
To the above aims the study of infilled frames for their structural use of infill walls was added as a special call for the addition of partners from countries that were at that time at the assessment stage for joining the EU. This allowed the Higher Technical Institute to join the project in 2002.
Hazard analysis of the City of Nicosia
Geological Survey Department of Cyprus (CY, coordinator)
United States Geological Survey Department (US)
Conservation of Historical Mediterranean Sites by Innovative Seismic-Protection Techniques (CHIME)
Università Degli Studi di Pavia (IT, coordinator)
Ecole Polytechnique de Tunisie (TUN)
Institut National de la Météorologie (TUN)
Institut National du Patrimoine (TUN)
Themos Demetriou – Civil Engineer (CY)
National Technical University of Greece (GR)
SIART – Sistemi Informativi per l’ Analyst del Rischio Territoriale ed Ambientale S.R.L. (IT)
University of Cairo (EGY)
http://cordis.europa.eu/project/rcn/52793_en.html
Restoration and Maintenance of Traditional Settlements
Cyprus Association of Civil Engineers and Architects (CY, coordinator)
Chamber of Engineers of Turkish Cypriots
1) Restoration and maintenance of traditional adobe construction
2) Restoration and maintenance of traditional stone masonry
3) Restoration and maintenance of traditional earth flat roofs
4) Restoration and maintenance of traditional tiled timber roofs
The objective of the four research teams would be the study of Cypriot traditional settlements, the pathology of their structures, proposals for their restoration and maintenance using traditional materials and methods and finding modern replacement materials and methods of the traditional ones. The Bi-communal Development Programme, which is funded with a grant from USAID (United States Agency for International Development) through UNOPS (United Nations Office for Project Services), was the vehicle that made this project possible. The project resulted in the book entitled “Restoration and Maintenance of Traditional Settlements”.